Who Created Lab Diamonds?
Posted by Koorosh Daneshgar on Jan 14th 2023

Lab-created diamonds are diamonds that are created in a laboratory setting rather than formed naturally in the earth. They have the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as natural diamonds and are virtually identical to them.
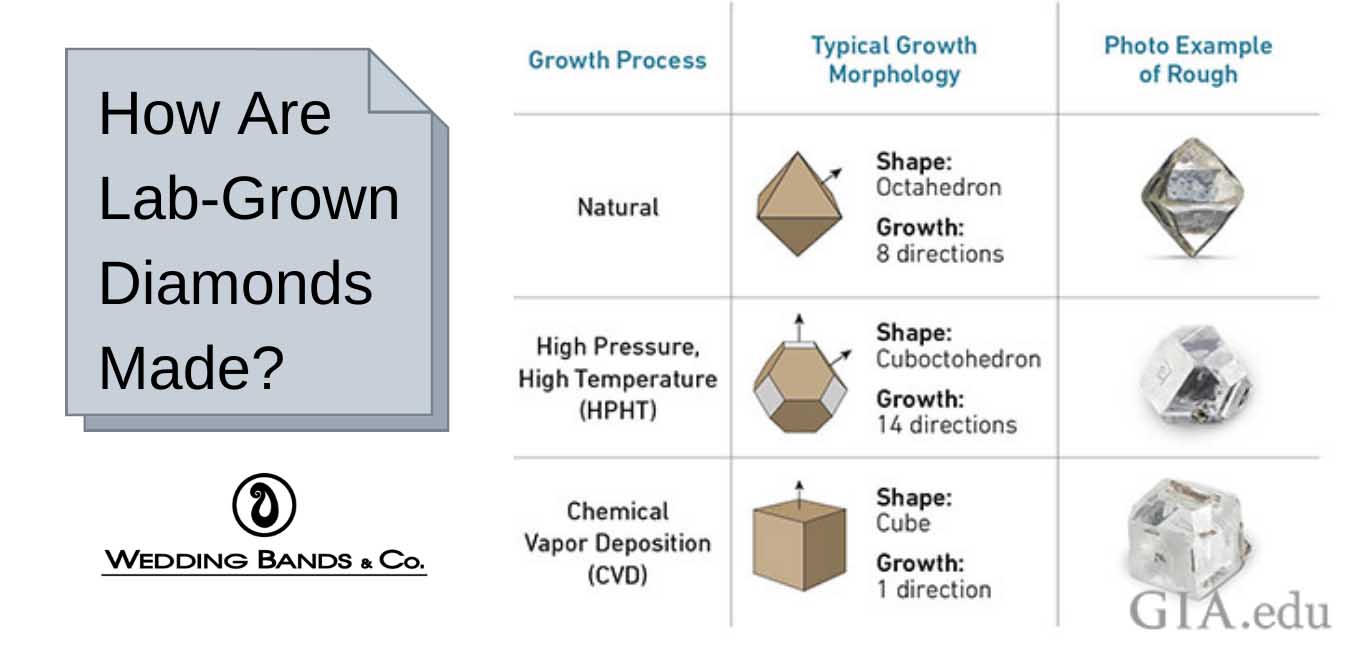
The history of lab-created diamonds dates back to the 1950s when scientists first began experimenting with the process of diamond synthesis. The first lab-created diamond was produced in 1955 by a team of scientists led by Dr. Henri Moissan, a French chemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1906 for his work on the chemical composition of meteorites. Moissan's team was able to create a small diamond by using a high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) method.

In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers at General Electric (GE) made significant advancements in the field of diamond synthesis. They developed a new method called chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which allows for the growth of diamonds in a controlled environment. This process involves introducing a mixture of gases, such as methane and hydrogen, into a chamber where they are exposed to a high-temperature plasma. The carbon in the gases then condenses and forms a diamond film on a substrate.
In the 1980s and 1990s, several companies began commercializing lab-created diamonds. Among them was Apollo Diamonds, which was founded in 2000 and became a leading producer of lab-created diamonds. The company was acquired by Luxuria in 2018.
Today, lab-created diamonds are produced by a number of companies around the world, including Element Six, Scio Diamond, and New Diamond Technology. They use both HPHT and CVD methods to create diamonds, and the process has become much more efficient and cost-effective over the years.
One of the major advantages of lab-created diamonds is that they are much more affordable than natural diamonds. They are also more ethically and environmentally friendly, as they do not require the mining and excavation of natural resources. Additionally, lab-created diamonds can be produced in a wide range of colors, such as blue, yellow, and pink, which are rare in natural diamonds.
However, lab-created diamonds are not without their criticisms. One of the main criticisms is that they are not as valuable as natural diamonds. Another criticism is that some companies may not disclose that their diamonds are lab-created, leading to confusion and potential deception for consumers.
To address these concerns, several organizations have established standards and guidelines for the labeling and grading of lab-created diamonds. The International Gemological Institute (IGI) and the Gemological Institute of America ( GIA) are two examples of organizations that provide grading and certification services for lab-created diamonds.
In conclusion, lab-created diamonds were first created in the 1950s by Dr. Henri Moissan, and since then have been developed by companies like General Electric and Apollo Diamonds. Today, lab-created diamonds are produced by a number of companies around the world using HPHT and CVD methods, with the process becoming more efficient and cost-effective over the years. While lab-created diamonds have many advantages, they also have their fair share of criticisms. But with the establishment of standards and guidelines for the labeling and grading of lab-created diamonds, consumers can now be better informed and make more informed decisions.
We'll help you to design your dream engagement ring without stress and spending countless hours searching for your perfect ring. All you need to do is click on "Free Consultation" to get started.

